Introduction to thread (Figure)

Figure 1 Types of threads
1. Basic tooth shape of ordinary triangular thread
The basic tooth shape of the ordinary triangular thread is shown in Figure 2. The names of the basic dimensions are as follows:
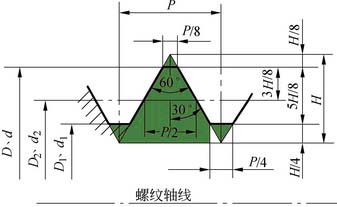
Figure 2 Ordinary triangular thread basic tooth type
D—large diameter of the internal thread (nominal diameter);
D—large diameter of the external thread (nominal diameter);
D2 — internal diameter of the internal thread;
D2—the diameter of the external thread;
D1 - internal thread diameter;
D1—outer thread diameter;
P-pitch;
H—the original triangle height.
There are three basic elements that determine the thread:
The angle of the profile α is the angle between the two sides of the internal thread of the axial section. Metric thread α=60 o , inch thread α=55 o .
Pitch P It is the distance of the corresponding point between two adjacent teeth in the axial direction.
Thread diameter D 2 (d 2 ) It is the diameter of an imaginary cylinder of the theoretical height H of the flat thread. The thread thickness and groove width at the middle diameter are equal. Only when the inner diameters of the inner and outer threads are the same, the two can fit well.
2. Methods and procedures for turning external threads
(1) Preparation work
1) When installing the thread turning tool, the cutting edge angle of the turning tool is equal to the thread profile angle α=60o, and the front angle γo=0o can ensure the tooth angle of the workpiece thread, otherwise the tooth angle will produce an error. Only when roughing or thread precision is not high, the rake angle can be γo=5o~20o. When installing the thread turning tool, the tool tip is aligned with the center of the workpiece, and the tool is used to match the tool to ensure that the angle bisector of the tool nose angle is perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece, and the tooth angle of the car is not deflected. As shown in Figure 3.
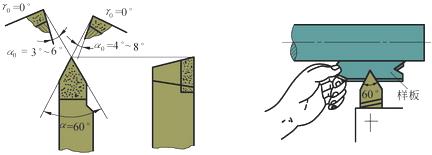
Figure 3 Thread turning tool geometry and tool setting
Next page
Plastic Rim, Metal Wheelbarrow Rim, Metal Rims
QINGDAO HYTANG HAND TRUCK CO.,LTD. , http://www.cnwheelbarrow.com
